Top 12 eCommerce Website Features
Functionality, design, and distinctive eCommerce platform features are crucial for eCommerce websites. It’s important to consider which eCommerce platforms are most likely to help you...
Puiblished: Jan 23, 2024 Updated: Jan 23, 2024
Databases, websites, SaaS (software as a service) apps, analytics tools, and more are among the many data sources and forms businesses can access. Unfortunately, because companies typically store this data, it can be challenging to draw out the insightful information concealed there, particularly when you’re seeking it to make more informed business decisions using data. That’s where ETL comes in.
You may find that standard reporting tools like Google Analytics are helpful, but eventually, you will need more space for your data analysis requirements. At this stage, consider developing a unique business intelligence (BI) solution, the basis of which will be the data integration layer.
ETL, which first appeared in the 1970s, is still the most used technique for integrating enterprise data. However, what precisely is ETL, and how does it operate? We detail it in this post and explain how your company can use it.
Extraction, transformation, and loading, or ETL, is a widely used method by businesses to merge data from several sources into just one database, data store, or data warehouse. ETL is used to aggregate data for analysis and decision-making, or you can utilize it to store data of legacy form, as is more common today.

For decades, businesses have been utilizing ETL. What’s different is that the target databases and data sources are now migrating to the cloud. Furthermore, streaming ETL pipelines are emerging and integrated with batch pipelines, i.e., they handle ongoing data streams in real time instead of batches of aggregated data. Some businesses use batch backfill or reconditioning pipelines in conjunction with continuous streaming procedures.
ETL is the term used to characterize the entire process by which an organization takes all of its data—both structured and unstructured, controlled by various teams from all over the world—and transforms it into a form you can use for business objectives.
Modern ETL systems of today have to keep up with the data’s increasing volume and speed. Furthermore, modern enterprise ETL solutions must now have the fundamental capabilities to ingest, enrich, and manage your transactions and support both structured and unstructured data in real-time from any source, whether on-premises or in the cloud.
ETL is a crucial tool for assembling all pertinent data in one location, analyzing it, and empowering managers, executives, and various stakeholders to use the information to make defensible business decisions. Brands frequently utilize ETL for the following tasks:
Making meaning of data, not explicitly creating analytical models, is possible with machine learning (ML). Instead, the machine learning system uses artificial intelligence algorithms to learn from data. ETL can be employed to consolidate the data into one place for machine learning.

The data warehouse is a repository created by combining data from many sources to examine it as a whole for commercial objectives. Data frequently moves to a data warehouse via ETL.
Moving your marketing data into one location, including social networking, web analytics, and customer data, will allow you to analyze it and create future strategies. This process is known as marketing data integration. Marketing data is gathered and prepared via ETL.
Database replication copies data into your cloud data warehouse from your source databases, which may include Oracle, Cloud SQL for MySQL, SQL Server from Microsoft, Cloud SQL for PostgreSQL, MongoDB, or others. You can use ETL to replicate the data, which may be a one-time or continuous procedure as your data changes.
The Internet of Things (IoT) is a broad network of interconnected electronic devices that have the ability to collect and send data using hardware-integrated sensors. IoT devices can include a wide variety of machines, including wearables and implanted devices, network servers, smartphones, and factory equipment. ETL facilitates data transfer from several IoT sources to a central location for analysis.
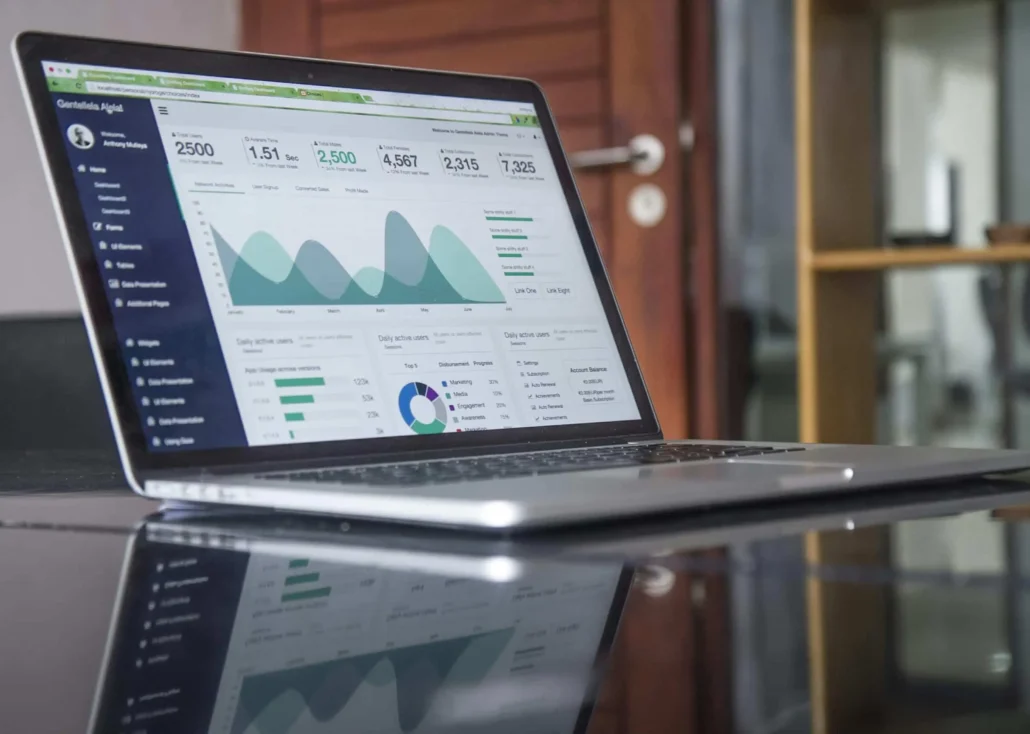
Businesses are migrating their data and apps from on-premises to the cloud to save costs, improve scalability, and secure data. ETL is frequently used to facilitate these migrations.
Data is periodically moved from the source system to the target system through extraction, transformation, and loading (ETL). There are three steps in the ETL process:
Extract, transform, and load (ETL) technologies are used in data extraction to replicate or extract raw data from various sources and put it in an area for staging. An interim storage location for the short-term storage of extracted data is a staging area (also known as a landing zone). Data staging facilities are frequently temporary spaces where brands remove contents once data extraction finishes. For troubleshooting purposes, the staging area may additionally keep a data archive.

The underlying change data collection method determines the frequency the system transfers data from the data source to the target data store. One of the three following methods most often works for data extraction.
In data transformation, the raw data is transformed and combined in the staging area using ETL (extract, transform, and load) technologies to get it ready for the target data warehouse. The following kinds of data modifications may occur during the data transformation step.
Fundamental transformations enhance the quality of the data by eliminating errors, clearing out data fields, or streamlining data. Here are a few examples of these modifications.

Business rules are used in advanced transformations to maximize the data for more straightforward analysis. Here are a few examples of these modifications.
ETL (extract, transform, and load) tools are used in data loading to transfer changed information from the staging area to the destination data warehouse. Most enterprises that employ ETL have an automated, well-defined, ongoing, batch-driven process. There are two ways to load the data.

All of the source data is converted and transferred to the information warehouse during full load. When you load data into the data warehouse for the first time from a source system, it’s usually the whole load.
When using incremental load, the ETL tool regularly downloads the difference, or delta, between the source and target systems. It saves the last extract date to ensure that only entries added after that date are loaded. You can implement incremental load in two ways.
ETL, also known as data extraction, load, and transform, is a crucial component of data management, particularly for companies that require data accuracy by all means. With the help of efficient and effective ETL techniques and tools, you can easily manage and align your data. Additionally, if you require management tools and software to help you optimize your data or website, contact us at Pimberly for the best services in town.


