Key Takeaways
- An AI-optimized tech stack ensures your data, systems, and workflows are ready for AI tools to deliver accurate, scalable results.
- The foundation of any AI-ready stack is clean, centralized, and structured data, not just new AI software.
- Product Information Management (PIM) plays a critical role in enabling AI across commerce, marketing, and operations.
What Is an AI-Optimized Tech Stack?
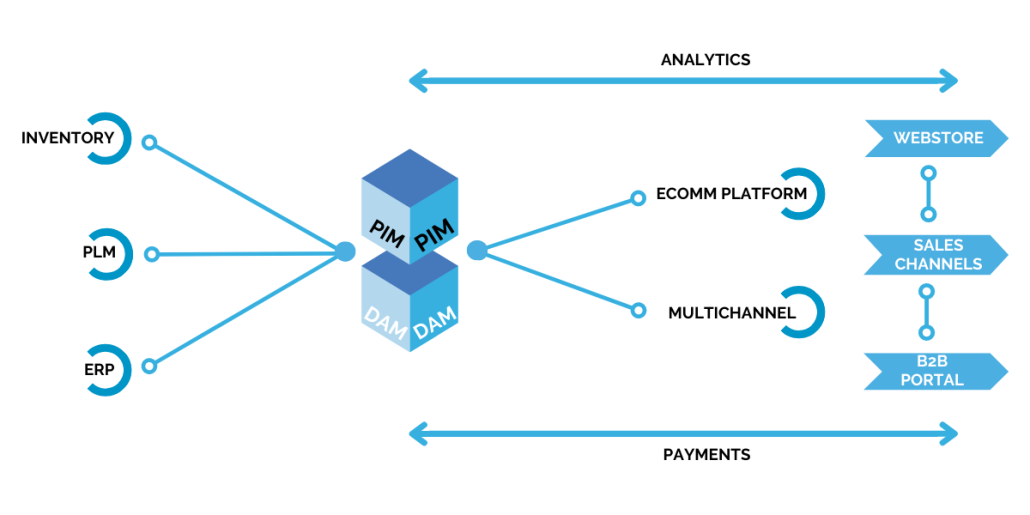
An AI–optimized tech stack is a collection of connected systems, platforms, and data sources designed to support artificial intelligence applications at scale. Rather than adding AI tools on top of disconnected software, an AI-optimized stack ensures that data flows cleanly, systems integrate seamlessly, and AI models can access accurate, up-to-date information.
In simple terms, it’s the difference between having AI and getting value from AI.
An AI-optimized tech stack typically includes:
- Centralized data management platforms
- API-driven integrations between systems
- Governance and security controls for AI usage
- Automation tools that reduce manual work
Without these elements, even advanced AI tools struggle to deliver meaningful outcomes.
Use Cases
Building an AI-optimized tech stack supports a wide range of business use cases, including:
- Automated content creation for product descriptions and marketing copy
- AI-driven search, recommendations, and personalization
- Demand forecasting and inventory optimization
- Data enrichment and attribute extraction
- Faster product launches across digital channels
These use cases all rely on structured, trustworthy data, which is why foundational systems matter more than AI features alone.
Why It Matters for Modern Commerce Teams
Challenge #1: Disconnected Systems and Data Silos
Most organizations did not design their tech stacks with AI in mind. Over time, teams added tools for ERP, eCommerce, DAM, CMS, and marketing automation—often without strong integration standards.
The result is:
- Duplicate product data
- Inconsistent attributes across channels
- Manual work to prepare data for AI tools
- AI outputs that lack accuracy or context
When AI pulls from fragmented data sources, it amplifies inconsistencies instead of fixing them.
Solution: Build the Stack Around Data Quality and Connectivity
An AI-optimized tech stack prioritizes data readiness first, ensuring that AI tools operate on a single source of truth.
This approach focuses on:
- Centralizing product and content data
- Standardizing attributes and taxonomy
- Connecting systems through APIs rather than manual exports
- Ensuring AI models receive structured, validated inputs
This shift allows AI to support teams instead of creating more rework.
Step 1: Centralize Your Core Data
Why Centralization Is the Foundation
AI tools are only as good as the data they consume. If product data lives across spreadsheets, ERPs, and eCommerce platforms, AI outputs will always be incomplete or inaccurate.
Centralizing data ensures:
- Consistency across all channels
- Faster access for AI models
- Reduced manual data cleanup
For commerce teams, this often means consolidating product information into a dedicated platform designed to manage complexity.
Real-World Example
A retailer using AI to generate product descriptions will see inconsistent results if attributes differ by channel. Centralized data ensures the AI always works from the same approved information.
Step 2: Structure Data for Machines, Not Just Humans
Why Structure Matters for AI
AI models rely on structured inputs such as attributes, taxonomies, and relationships. Free-form text and inconsistent naming conventions make it harder for AI to interpret meaning.
Structuring data includes:
- Standardized attribute names
- Clear product hierarchies
- Defined relationships between products, variants, and assets
- Controlled vocabularies for key fields
This structure allows AI to understand context instead of guessing.
Use Case Example
When attributes like size, material, or compatibility are structured, AI can:
- Power faceted search more accurately
- Generate compliant product descriptions
- Support recommendation engines
Without structured data, AI tools often produce generic or misleading outputs.
Step 3: Connect Systems Through APIs
Why Integration Enables Scale
An AI-optimized tech stack depends on real-time connectivity between systems. Manual imports and exports slow down workflows and increase the risk of outdated information.
API-driven integrations allow:
- Continuous data synchronization
- Faster onboarding of new AI tools
- Reduced dependency on custom scripts
This flexibility ensures your stack can evolve as AI capabilities improve.
Example in Practice
When PIM, DAM, eCommerce platforms, and AI tools share data through APIs, teams can update product information once and push changes everywhere—while AI tools immediately reflect those updates.
Step 4: Apply Governance and AI Guardrails
Why Governance Is Critical for AI Adoption
As AI becomes embedded in daily workflows, organizations must ensure responsible usage. An AI-optimized tech stack includes guardrails that control how data is processed and shared.
Key governance considerations include:
- Data privacy and access controls
- Clear rules for AI-generated content
- Transparency into how AI outputs are created
- Alignment with regional regulations
These controls build trust internally and externally.
Practical Benefit
Governed AI workflows allow teams to scale automation without risking brand consistency, compliance, or data security.
Step 5: Optimize Workflows With Automation
Moving Beyond One-Off AI Experiments

True AI optimization happens when automation is embedded into everyday workflows. Instead of treating AI as a novelty, teams should use it to reduce repetitive tasks.
Automation opportunities include:
- Bulk enrichment of product attributes
- Automated content generation and translation
- Image tagging and metadata creation
- Validation checks before publishing
These workflows free teams to focus on strategy instead of manual upkeep.
Outcome for Teams
With automation in place, organizations move faster, reduce errors, and improve time to market—key advantages in competitive eCommerce environments.
AI-Optimized Tech Stack and PIM: Why Product Information Matters
An AI-optimized tech stack relies heavily on high-quality product data, which is where Product Information Management plays a central role. PIM acts as the foundation that connects AI tools to accurate, enriched, and structured product information.
By managing attributes, assets, and workflows in one place, PIM ensures AI outputs remain consistent across channels. It also provides the governance and structure AI tools need to scale responsibly.
Without PIM, teams often rely on fragmented data sources, making AI initiatives harder to maintain and less reliable over time.
FAQs
What is an AI-optimized tech stack?
An AI-optimized tech stack is a connected set of systems designed to support AI tools with clean, structured, and centralized data, enabling accurate and scalable AI outcomes.
How is an AI-optimized tech stack different from a traditional tech stack?
Traditional stacks focus on operational needs, while AI-optimized stacks prioritize data readiness, integration, and governance to ensure AI tools deliver consistent value.
Do you need AI tools to build an AI-optimized tech stack?
Not immediately. Many organizations start by improving data structure and integration so they are ready to adopt AI tools when needed.
Why is PIM important for AI initiatives?
PIM centralizes and structures product data, giving AI tools reliable inputs and ensuring consistent outputs across channels.
Key Takeaways for Teams Building an AI-Optimized Tech Stack
To summarize, building an AI-optimized tech stack is less about chasing new AI tools and more about getting the foundation right.
What this means for you:
- Centralize and structure your data before scaling AI
- Invest in integrations that keep systems connected
- Apply governance to ensure responsible AI usage
- Use automation to reduce manual work and speed execution
Next steps involve assessing where data silos exist today and identifying which systems need to be better connected to support future AI initiatives.